Practical guidance on using generative AI in Business
As early as 1947, the visionary Alan Turing foresaw the potential for computer intelligence. Fast forward 50 years to 1997, and IBM’s Deep Blue made history by defeating the world chess champion, Garry Kasparov, marking a significant milestone in AI development. Today, AI is revolutionizing the way we start tasks and brainstorm, with generative AI (gen AI) leading the charge.
According to McKinsey’s latest report, 74% of organizations are actively integrating AI into their processes. However, with the average cost of training generative, research, or detection AI models estimated at $78 million, companies turn to third-party AI solutions. This rapid adoption brings a set of challenges.
No firm wants to be left behind. In this article we give practical advice in managing accuracy and risk. It’s essential to balance the benefits of AI with some risk mitigation strategies as we continue to learn and adapt.
Context of Generative AI in 2023-2024
Generative AI is created by training algorithms on vast amounts of data to recognize patterns and structures. For instance, if the goal is to generate new images, the AI is fed millions of pictures, which it analyzes to understand common features and relationships. Through this process, known as training, the AI learns to identify and replicate these patterns. Once trained, the AI can generate new content by combining, predicting the learned patterns, similar to how a person might use their knowledge and creativity to produce something new.
This technology continually improves as it processes more data and receives positive or negative feedback. Over time these algorithms will also learn undesirable or even faulty patterns.
Understanding and Dealing with Inaccuracy
In the below image, we can observe the mangled hands generated as a visible and undesirable outcome. Often, undesirable outcomes manifest without being immediately apparent. For instance, an AI can exhibit gender bias, such as displaying a light-colored male 9 times out of 10. AI in the coming year will get better by applying, Filtering data, Re-training, Incorporating Human Feedback and so on.
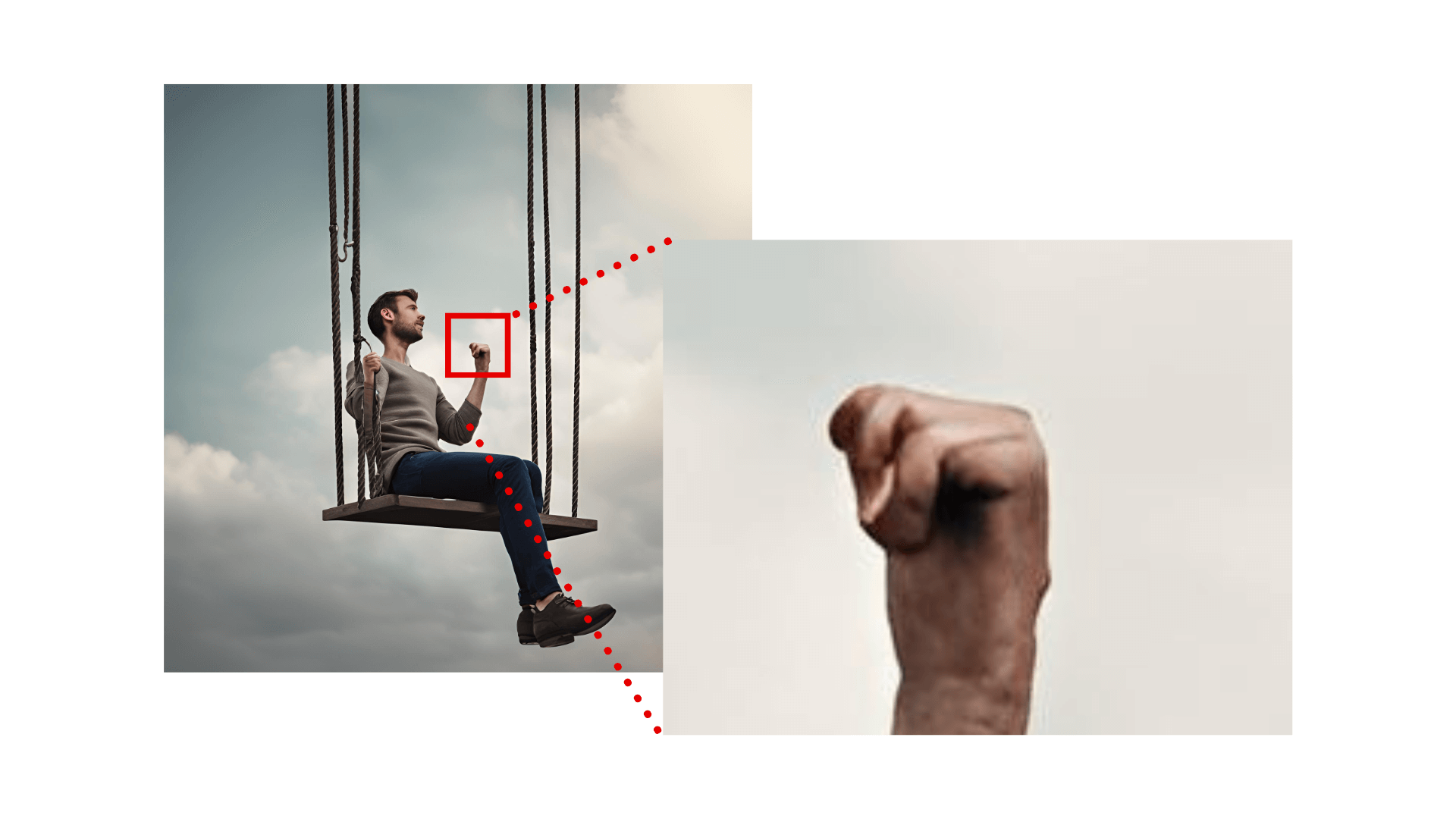
So, now what? At the workplace we should be aware that the more complex the task the chance that a inaccuracy, undesirable outcome is introduced grows. We need to incorporate human oversight at critical points in any AI workflow. Fact check output. Ensure that humans can intervene, review, and correct the AI’s outputs before they are applied.
Practical guidance 1: Human-in-the-Loop
- Critical Checkpoints: Have human experts review AI outputs at key stages before final decisions or actions are taken.
- Explainability: Where possible ask the AI to provide explanations and sources for its conclusions.
Commercial Data and Privacy
It feels so tempting to upload a critical business report into any available AI and ask for a summary. Tim O’Reilly, CEO of O’Reilly Media, regularly posted, “If you aren’t paying for it, you aren’t the customer, you’re the product.” This idea, dating back to 1973, holds true for unpaid services and even some paid AI services.
Many AI services use user feedback and input to learn and refine output. While they may not reproduce the exact document you entered, they can use it to serve another customer. To comfortably share information, you need to start reading usage and privacy policies. For example, Copilot offers a reasonable privacy statement (reference 5) for logged-in paying users. Personally, I would not enter critical business information or datasets into a third-party AI. Instead, consider the following techniques to minimize potential impact:
- Samples or Fake Data Only: Upload only a small, non-sensitive subset of your data.
- Score the Input Based on CIA Rating: Evaluate the data’s Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability (CIA) rating to assess its sensitivity before sharing.
- Anonymize Data: Remove or obfuscate any personally identifiable information (PII) like names, groups, dates, addresses, and so on.
- Open Source Models: Be aware that there are amazing task-specific open source AI models available that can run on a decent PC.
By following these techniques, a business can minimize the risk of exposing critical information while leveraging AI services (to find patterns) effectively.
Practical Guidance 2: Limited Data Exposure
- Use Anonymized Data Samples: Use anonymized data samples to find patterns without exposing sensitive information.
- CIA Rating: Score data based on Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability to determine what can be shared without consequences.
- Reputable vendor selection: Use a reputable service or fall back to a contained system.
AI as a Training Subject in the Workplace.
Just as companies mandate IT security and GDPR compliance training, there is a growing need to consider AI training for employees. To get more benefits and also understand basic technology concepts. Tools like ChatGPT are designed to be intuitive, capable of understanding natural language. So, why is there a necessity for training on these AI tools?
My own research and questionnaires reveal that about 43% of employees use AI on a weekly basis. 82% claim they have received GDPR training while only 12% have received awareness training on the capabilities and risks of AI. These statistics highlight a significant gap. Preparedness for the AI revolution. This underscores an urgent need for training programs or at least company guidance document to help employees harness AI tools.
Practical Guidance 3: AI usage guidelines
- AI Awareness Training: Incorporate AI awareness training into the company on-boarding. This should cover the basics of AI, its applications, and potential risks.
- Guidelines: Develop some policies regarding the use of AI tools in the workplace
Concluding
No firm wants to be left behind and rightfully so. Start learning! Automating or brainstorming tasks is today but what tomorrow? Whether you’re buying AI from a third party or building capability in house, we hope this guide can help set you on a path to using AI reliably and safely within your business
References:
- https://www.dcsc.tudelft.nl/~sc4081/2018/assign/pap/alphago_paper2.pdf
- https://www.mckinsey.com/capabilities/quantumblack/our-insights/the-state-of-ai
- https://www.proso.com/dl/Samonas.pdf
- https://edge.sitecorecloud.io/avanadeinc2-dotcom-prod-19a8/media/project/avanade/avanade/assets/research/generative-ai-readiness-report.pdf
- https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/copilot/privacy-and-protections#commercial-data-protection
- https://openai.com/policies/eu-privacy-policy/
- https://www.who.int/news/item/28-06-2021-who-issues-first-global-report-on-ai-in-health-and-six-guiding-principles-for-its-design-and-use
@ 2024 semantize.nl Roland Broekema